Before real-time data, businesses had to rely on batch processing to collect and analyze large sets of data in periodic intervals. While batch processing was effective for historical analysis, it lacked the immediacy necessary for fast, actionable insights. With the rise of real-time data, businesses can now process information continuously as it arrives, enabling real-time decision-making. Additionally, it allows companies to respond to events instantly, improving operational efficiency and customer experiences.
According to McKinsey, high-performing companies are 70% more likely to have data broadly accessible to employees, enabling faster decision-making compared to their counterparts. Additionally, 92% of business leaders report plans to increase investment in real-time data analytics in the near future.

As businesses continue to evolve and demand faster, more dynamic insights, the shift towards real-time data becomes not just an advantage but a necessity. To understand the impact and mechanics of real-time data, we’ll walk you through how it fundamentally differs from traditional methods.
What is real-time data?
Real-time data refers to information that is captured, processed, and delivered to end users with minimal latency. Another signature of real-time data is that you can collect from a wide range of sources, such as cameras, social media feeds, sensors, operational systems (e.g., ERP systems), and databases. According to Dmitriy Rudakov, Director of Solution Architecture at Striim, the difference between real-time data is “its latency and how soon the user receives the data. So in some cases it’s milliseconds and in some cases it’s hours, but the main idea is that events arrive as soon as network and source speed allows. There’s typically a defined service level agreement (SLA).”
This type of data provides a current view of events as they happen, enabling businesses to make informed decisions in the moment. Whereas with batch processing data is collected and analyzed at set intervals, real-time data is continuously streamed and updated, ensuring that the latest insights are always available.
This immediacy of real-time data is crucial for a variety of applications, from monitoring stock market changes to tracking customer behavior on e-commerce platforms. For instance, in industries like finance and healthcare, real-time data enables immediate responses to potential issues, such as fraud detection or patient monitoring. In retail and e-commerce, it allows for dynamic pricing adjustments, personalized customer experiences, and real-time inventory management.
By leveraging real-time data, businesses can not only react to events but also predict trends and opportunities, allowing them to stay ahead in fast-paced environments. Stream processing systems make this possible by processing data continuously as it is generated, rather than waiting for batches of information. This capability gives organizations a significant edge in improving operational efficiency, enhancing customer experiences, and making proactive decisions.
Real-time data can be categorized into the following types:
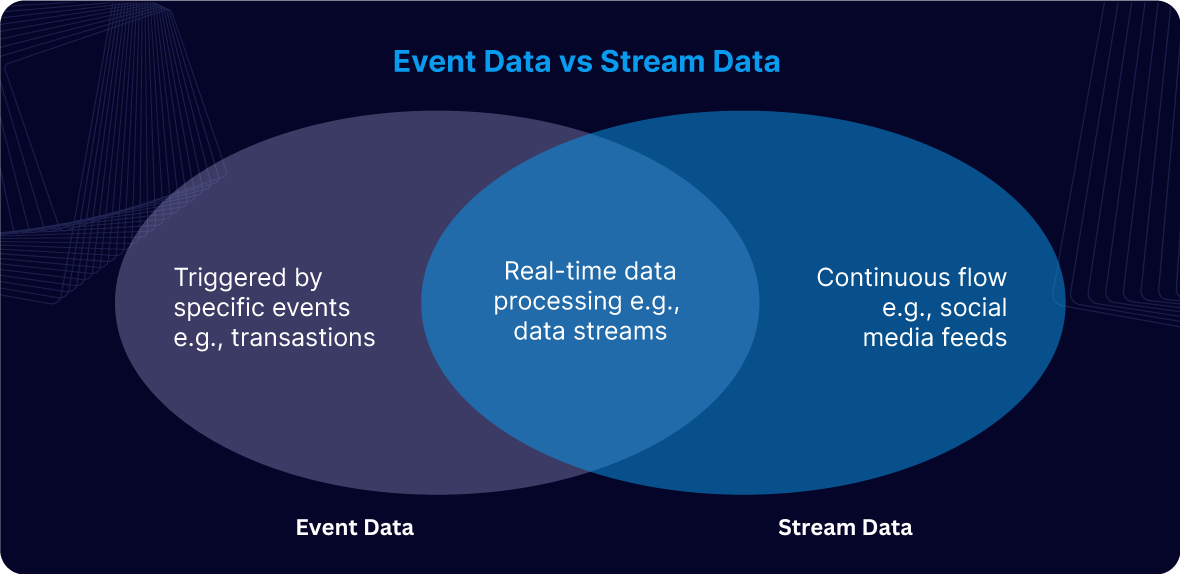
- Event data: This refers to data generated in response to specific, well-defined events or conditions within a system. For example, when a user makes a purchase on an e-commerce platform, event data is generated to capture the details of that transaction.
- Stream data: This type of data is continuously produced in large volumes, without any defined beginning or end. It includes real-time data flows from sensors, social media feeds, or network traffic.
What are Examples of Real-Time Data?
Examples of real-time data in an organization include system malfunction alerts, tracking the locations of assets or moving objects, and telemetry readings. This data can be sourced from both applications and sensors.
By using real-time data from applications (e.g., user interactions, page views, auction bids) and sensors (e.g., equipment temperature, system overload warnings), organizations can make faster decisions and maintain operational efficiency.
Let’s walk through some real-time data examples to demonstrate why it’s impactful.
American Airlines exemplifies the power of real-time data by using it to streamline their flight operations. Managing over 5,800 daily flights, they rely on a sophisticated real-time data hub that integrates Striim, MongoDB, Azure, and Databricks. This hub captures and processes operational data, such as aircraft telemetry and maintenance needs, enabling the TechOps team to monitor and react to potential issues immediately. By leveraging this real-time data infrastructure, American Airlines ensures safe, efficient operations and an enhanced customer experience across their global network.
In the retail sector, legendary brand Macy’s faced significant challenges due to fragmented data across systems like mainframe and Oracle databases, leading to inconsistencies, high costs, and slow application development. Striim provided a solution by replicating real-time data to Google Cloud services like Cloud Spanner and BigQuery, creating a unified source of truth. This allowed Macy’s to streamline inventory management, reduce costs, ensure consistent customer experiences across channels, and accelerate time to market, supporting their overall digital transformation goals.
Historical vs Real-Time Data: What’s the Difference?
Historical data plays a crucial role in batch processing, as it is collected, processed, and stored over time in an organization’s data repository. Typically analyzed in large volumes, historical data helps identify trends and insights, but it is not available for immediate decision-making. Unlike real-time data, which is continuously generated and offers up-to-date insights, historical data is bounded by a specific timeframe.
Say you want to plan your route to get home from the airport. While historical data can analyze past traffic patterns for route planning, it cannot adapt to sudden changes like a closed lane, highlighting the limitations of relying solely on historical information. In contrast, applications fueled by real-time data, such as Google Maps, leverage current data to provide instant updates and optimize travel routes efficiently.
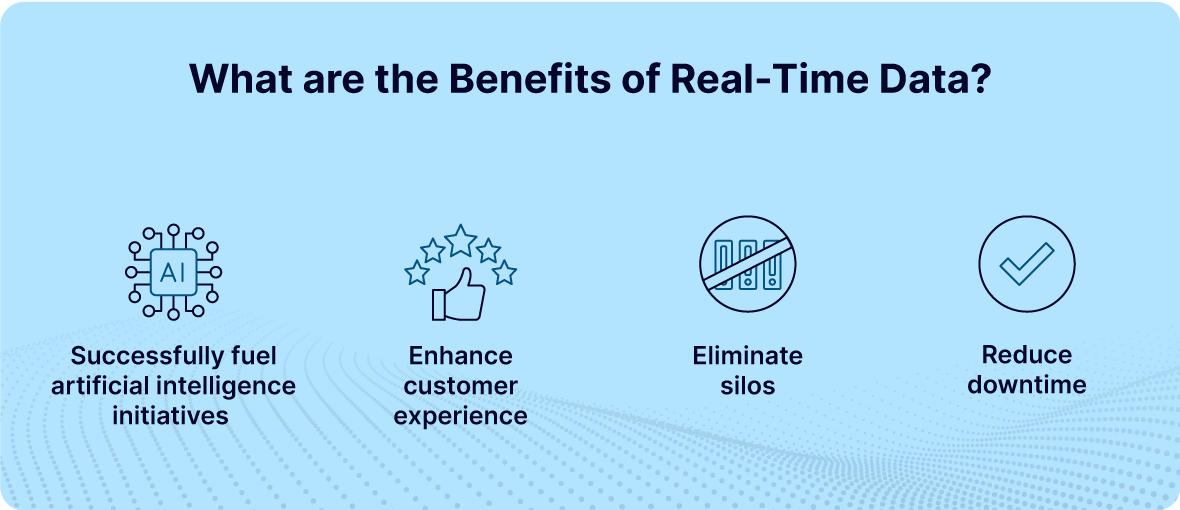
What are the Benefits of Real-Time Data?
Real-time data allows companies to adopt a proactive approach. Access to real-time data means they can make decisions based on the latest data to address their inefficiencies and empower their end-users to be well informed.
Successfully Fuel Your Artificial Intelligence Initiatives
The future of AI is real-time data. Real-time data is essential for advancing AI initiatives because it enables instant processing and continuous learning.
Unlike traditional batch processing, which delays data analysis, real-time data provides immediate access to current information, allowing AI systems to make data-fueled decisions and adapt quickly. This is because, with real-time data, your models are trained on the latest, most up-to-date information.
Enhance Customer Experience
To enhance customer experience, leveraging real-time data is crucial, especially when it comes to delivery tracking. A study conducted by Descartes Systems Group reveals that 90% of consumers expect real-time tracking updates.
By utilizing real-time data, businesses can address customer inquiries promptly and provide insights from drivers, deliveries, and operations. This transparency allows customers to track their orders from confirmation to delivery, ensuring they are informed throughout the process. Additionally, features such as instant communication with delivery drivers can improve convenience by accommodating customers’ preferred delivery schedules.
For instance, UPS Capital harnessed Striim’s real-time data streaming technology with Google BigQuery to enhance both delivery security and customer satisfaction. By streaming data instantly from multiple sources, Striim enabled immediate risk assessments and proactive decision-making. Integrated with BigQuery’s analytics and machine learning, this real-time data predicted delivery risks and optimized logistics strategies. The DeliveryDefense™ Address Confidence system, fueled by real-time insights, assigned confidence scores to delivery locations, significantly improving predictive accuracy. These real-time capabilities not only enhanced security but also increased customer satisfaction by ensuring timely deliveries, providing transparency throughout the process, and safeguarding customers’ packages.
Eliminate silos
When relying on historical data, teams often encounter information silos, where departments operate independently, unaware of each other’s current operations. Without real-time data, this disconnect can lead to inaccurate decision-making.
For instance, a customer service representative might inform a customer that their delivery will arrive on time, based on outdated information. However, if the product went out of stock just a few hours earlier, the customer may experience delays and frustration, leading to a poor customer experience. By contrast, real-time data allows for up-to-the-minute accuracy, enabling more precise answers and ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction.
Reduce downtime
Real-time data empowers businesses to take a proactive approach in managing assets by enabling them to predict, prevent, and address failures before they escalate. By continuously streaming data from various systems, companies can monitor machinery, infrastructure, and service levels in real time, allowing early detection of issues like equipment failure or service spikes. This ensures swift action, preventing minor inefficiencies from becoming larger, costlier problems, ultimately reducing downtime and optimizing performance.
Circling back to American Airlines, it used Striim’s real-time data streaming to optimize flight operations by tracking data from multiple sources such as aircraft sensors and weather conditions. This enabled the airline to anticipate potential disruptions and proactively adjust flight routes or schedules, reducing delays and improving customer satisfaction .
Use Striim to power your real-time data architecture
Real-time data is no longer optional—it’s essential for modern businesses looking to stay competitive. Gone are the days when real-time systems were considered too expensive for widespread adoption. With advancements in memory, CPUs, and cloud technologies, real-time data processing is now both affordable and scalable, making it a must-have for organizations of all sizes. “Striim’s data collectors such as CDC readers due to its design allow real time data delivery without impacting the source systems,” shares Dmitriy Rudakov.
A real-time data integration platform like Striim can help you harness the power of real-time data to optimize your operations. By integrating data instantly from various sources—whether it’s sensors, databases, log files, or data warehouses—Striim ensures that your data is always current and actionable. Additionally, it enables you to pre-process and enrich data with streaming analytics, giving your organization the ability to make faster, smarter decisions.
Ready to see the difference of real-time data firsthand? Schedule a demo to explore Striim with an expert.