More than a decade ago, Microsoft launched Project Florence. This was a research wing created to resolve issues developers faced while building large-scale applications within Microsoft. After some time, Microsoft realized developers around the world also faced these challenges while creating globally distributed applications. This led to the release of Azure DocumentDB in 2015. Over the years, it received more features and updates and evolved into Azure Cosmos DB. Thanks to the countless benefits of Cosmos DB, it’s one of the most popular NoSQL databases today.
Cosmos DB is a NoSQL database designed to handle large workloads on a global level. It offers a plethora of features that can make database creation and management easier, and it also ensures that your database is scalable, reliable, and available.
1. You can use APIs to store data in different models
A relational database is only required when you need a normalized data structure — comprised of rows and columns. Otherwise, you can take advantage of Cosmos DB’s multi-model capabilities. A multi-model database enables you to store data in multiple ways — relational, document, key-value, and column-family — in a single and integrated environment. When it comes to Cosmos DB, you can use APIs of different databases natively and use them to store data.
- SQL API: SQL API is the default Cosmos DB API. You can use it to write SQL to search within JSON documents. Unlike other Cosmos DB APIs, it also supports server-side programming, allowing you to write triggers, stored procedures, and user-defined functions via JavaScript.
- MongoDB API: MongoDB is one of the most popular NoSQL databases, and you can integrate with Cosmos DB by using MongoDB’s wire protocol via MongoDB API. This way, you can use MongoDB’s existing client drivers. Moreover, you can use this API to migrate your current MongoDB applications to Cosmos DB with some basic and quick changes.
- Cassandra API: Apache Cassandra is an open-source NoSQL wide column store database, which can be queried with a SQL-like language — Cassandra Query Language (CQL). Cosmos DB’s Cassandra API allows you to use CQL and Cassandra’s drivers and tools, such as cqlsh.
- Gremlin API: Cosmos DB Gremlin API uses Gremlin — a functional query language — to offer a graph database service. You can also use Gremlin to implement graph algorithms.
- Table API: Azure Table Storage is a NoSQL datastore used for storing a large amount of non-relational and structured data. You can use Table API to store and query data from Azure Table Storage.
2. You can replicate data globally for multiple regions
Typically, when you’re looking to create a large-scale globally distributed application, it’s accompanied by considerable work. Building such applications requires you to spend plenty of time planning a multi-center data environment configuration that can smoothly support your application.
Cosmos DB has been built as a globally distributed database, which means you don’t have to waste time planning your multi-center environment. You can configure Cosmos DB to replicate your data to all of your targeted regions. To minimize latency, look into where your users live and place the data closer to them. Cosmos DB will then deliver a single system image of your global database and containers, which are read and written locally by your application.
All global applications aim for high availability, so users of that data can access it without interruption. With Cosmos DB, you can run a database in several regions at once, which can improve your database’s availability. Even if a region is unavailable, Cosmos DB automates the handling of application requests by assigning them to other regions. This global distribution of data is turnkey — you can add or remove one or more geographical regions with a brief API call or a few clicks.
For instance, if you manage a SaaS application, it’s likely to get customer requests from around the world. Formats that store and track user experiences, such as session states, product catalogs, and JSON require accessibility with low latency. Cosmos DB’s globally distributed storage can help you store this data.
3. You can create social media applications
Social media is one of the niches where developers use Cosmos DB to store and query user generated content (UGC) — content users generate in the form of text, reviews, images, and videos. For instance, you can store the data of your social media network’s user ratings and comments in Cosmos DB. Blog posts, tweets, and chat sessions are also part of UGC.
UGC is a combination of free-form text, relationships, tags, and properties that are not governed by an inflexible structure. That’s why UGC is categorized as unstructured data. A relational database can’t store UGC due to its strict schema limitations. A NoSQL database like Cosmos DB can store UGC data more easily because it’s schema-free. Developers have more control to adapt their database to different types of data. In addition, this form of database also requires fewer transformations for data storage and retrieval than a relational database.
Since Cosmos DB is schema-free, you can use it to store documents with different and dynamic structures. For instance, what if you want your social media posts to contain a list of hashtags and categories? Cosmos DB can manage this by adding them as attributes without requiring any additional work. Unlike relational databases, you can make object mapping simple by setting comments under a social media post with a parent property in JSON. Here’s what it would look like:
{
“id”:”4322-bte4-65ut-200b”,
“title”:”My first post!”,
“date”:”2022-05-08″,
“createdBy”:User5,
“parent”:”dv13-sft3-353d-655g”
}
You have to enable your users to search and find content easily. For that, you can use Azure Cognitive Search to implement a search engine. This process doesn’t require you to write any code and is completed within a few minutes.
For storing social media followers, you can use the Gremlin API to use vertexes for each store. Similarly, you can set edges to create the relation of user A following user B. You can also make suggestions to users with common interests by adding a graph.
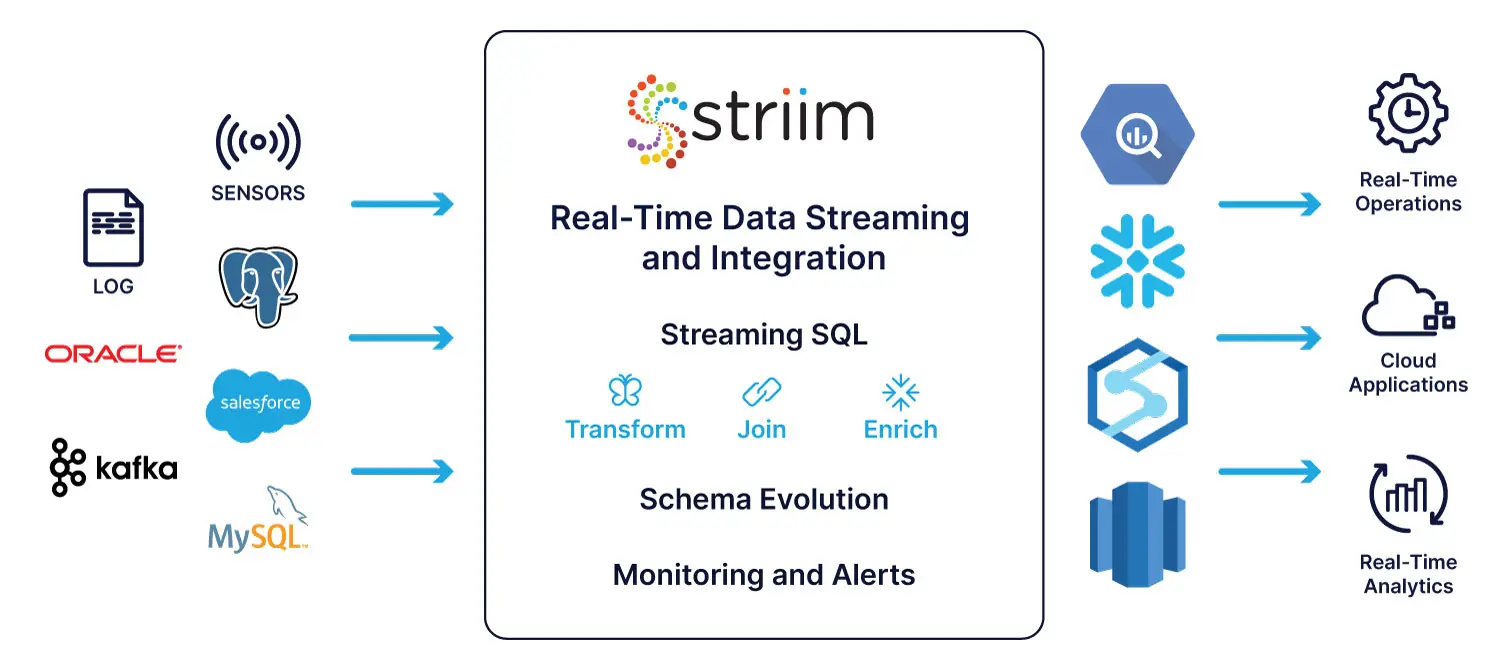
Use Striim’s native integration to unlock all the benefits of Cosmos DB
For all the benefits of Cosmos DB, there are some minor issues that plague its users. These users struggle to find native integration that supports document, relational, and non-relational databases as sources, hampering data movement into Cosmos DB. Another issue that plagues Cosmos DB users is the use of Batch ETL methods, which are unsuitable for a few use cases. Batch ETL methods read periodically from source data and write to target data repositories after a fixed time. That means all the data-driven decisions that are made after performing analytics on the target data repository are based on relatively old data.
As a unified data integration and streaming platform, Striim connects data, clouds, and applications with real-time streaming data pipelines.
Striim has come up with a solution for both problems. It offers native integration with Cosmos DB, which means you can use Striim to move data from a wide range of data sources, including Salesforce, PostgreSQL, and Oracle to Cosmos DB. Striim also supports real-time data movement, allowing you to replace your batch ETL methods in applications that need real-time analytics.