Connecting from Striim to MongoDB with SSL
Striim's MongoDB Reader uses Java drivers to connect to MongoDB. An SSL handshake must be performed while creating a connection.
If the certificate of the server is signed by a Certificate Authority that is known to the JRE, the certificate presented for the server is automatically trusted by the JRE and there is no need to set an extra trust store by the user. For example, connecting to a MongoDB Atlas node does not require setting the trust store or key store. A SSL connection to MongoDB nodes whose certificate was signed by a CA that is not recognised by the JRE requires the handshake with the trust store and/or key store.
Note
Sometimes setting only the truststore might be required. This is determined by the server configuration. There is no need to set up the keystore if sslAllowConnectionsWithoutCertificates is enabled in the MongoDB server.
Striim accepts the keystores in JKS format by default.
Creating the truststore
The truststore is a Java cryptographic store that contains certificates of the certificate authorities (CAs). It can contain multiple certificates. For a successful handshake, the truststore should contain the certificates of all the CAs that signed the certificates of parties that are involved. If the same CA signed the certificate of both the parties, only one certificate (that of the CA) needs to be present in the truststore.
The following steps include creating a truststore. In order to prevent the truststore from assuming the metadata from a specific certificate, the it is created using a dummy certificate which is immediately deleted. Following this step the certificate of the CA(s) can be imported into the truststore with unique aliases.
Note that the following steps create the truststore in JKS format.
Create a truststore based on a temporary key
keytool -genkey -keyalg RSA -alias dummyca -keystore truststore.ks
This interactive utility creates a default certificate. This is a temporary certificate that is subsequently deleted by the -delete command, so it does not matter what information you enter here:
Enter keystore password: Re-enter new password: What is your first and last name? [Unknown]: What is the name of your organizational unit? [Unknown]: What is the name of your organization? [Unknown]: What is the name of your City or Locality? [Unknown]: What is the name of your State or Province? [Unknown]: What is the two-letter country code for this unit? [Unknown]: Is CN=Unknown, OU=Unknown, O=Unknown, L=Unknown, ST=Unknown, C=Unknown correct? [no]: yes Enter key password for <dummyca> (RETURN if same as keystore password): Re-enter new password:
Be sure to record the password for future use.
Delete the entry to create an empty truststore:
keytool -delete -alias dummyca -keystore truststore.ks
Import each CA certificate into the trust store with a different alias:
keytool -import -v -trustcacerts -alias ca -file ca.pem -keystore truststore.ks
The certificates of all CAs must be present in the truststore file truststore.ks.
Creating the keystore
The keystore is a Java cryptographic store that contains certificates of the server(s) or all the participants in the communication. It can contain multiple certificates. The certificates of all the MongoDB server nodes should be imported. The certificate of the client may also be included depending on the setup.
The pem file of each participant should be converted into FIPS approved format (PCKS #8 or above) before importing into the key store.
The following steps include creating a trust store. In order to prevent the trust store from assuming the metadata from a specific certificate, the trust store is created using a dummy certificate which is immediately deleted. Each certificate should have a different alias in the key store.
The following steps create the trust store in JKS format.
Convert each .pem file into PCKS12 format (replace
<n>with the number in each file name).openssl pkcs12 -export -out server<n>.pkcs12 -in server<n>.pem
Create a truststore based on a temporary key:
keytool -genkey -keyalg RSA -alias dummyca -keystore truststore.ks
This interactive utility creates a default certificate. This is a temporary certificate that is subsequently deleted by the -delete command, so it does not matter what information you enter here:
Enter keystore password: Re-enter new password: What is your first and last name? [Unknown]: What is the name of your organizational unit? [Unknown]: What is the name of your organization? [Unknown]: What is the name of your City or Locality? [Unknown]: What is the name of your State or Province? [Unknown]: What is the two-letter country code for this unit? [Unknown]: Is CN=Unknown, OU=Unknown, O=Unknown, L=Unknown, ST=Unknown, C=Unknown correct? [no]: yes Enter key password for <dummyca> (RETURN if same as keystore password): Re-enter new password:
Be sure to record the password for future use.
Delete the entry to create an empty truststore.
keytool -delete -alias dummy -keystore keystore.ks
Import the certificate of each participant into the key store with a different alias:
keytool -v -importkeystore -srckeystore server<n>.pkcs12 -alias server<n> -srcstoretype PKCS12 -destkeystore keystore.ks -deststoretype JKS
The certificates of all participants must be present in keystore.ks.
Upload the stores to Striim
The generated stores (truststore and/or keystore) must be uploaded to the Striim server.
Note the uploaded location of each file.
Configure the Security Config property
Security Config is a MongoDB Reader property in which the parameters are separated by semicolons (;). The parameter name and value are separated by colons (:)
We recommended you store the Security Config value in the Striim vault and use the Vault Key to refer to it.
Security Config properties
Depending on the configuration some or all of the following parameters might be required to prepare Security Config. Only the parameters that actually have a value need to be supplied in Security Config.
Parameter Name | Description | Default | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|---|
TrustStore | The location of the trust store file in the Striim server. For example: Platform/UploadedFiles/truststore.ks | No | |
TrustStorePassword | Passphrase to open the trust store, if present | No | |
TrustStoreType | The key store type of the uploaded file specified in the TrustStore parameter. Only the key store algorithms that are supported by the JRE can be provided. Apart from JKS, PKCS12 is a common key store type. | JKS | No |
KeyStore | The location of the key store file in the Striim server. For example: Platform/UploadedFiles/keystore.ks | No | |
KeyStorePassword | Passphrase to open the key store. KeyStorePassword is required if a KeyStore file is provided. | Yes, if KeyStore is provided | |
KeyStoreType | The key store type of the uploaded file specified in the KeyStore parameter. Only the key store algorithms that are supported by the JRE can be provided. Apart from JKS, PKCS12 is a common key store type. | JKS | No |
SecureSocketProtocol | The SSL protocol used to connect to MongoDB. A specific protocol version supported by the JRE can be specified, if required. | TLS | No |
Security Config use case examples
Providing only TrustStore information:
TrustStore:Platform/UploadedFiles/truststore.ks;TrustStorePassword:admin1Providing KeyStore and TrustStore:
KeyStore:Platform/UploadedFiles/keystore.ks;TrustStore:Platform /UploadedFiles/truststore.ks;TrustStorePassword:admin1;KeyStorePassword:admin1
Providing a KeyStore in PKCS format and TrustStore in JKS (default) format:
KeyStore:Platform/UploadedFiles/keystore.ks;TrustStore:Platform /UploadedFiles/truststore.ks;TrustStorePassword:admin1; KeyStorePassword:admin1;KeyStoreType:PKCS12
Using Striim Vault to store the Security Config
Create a vault from the console:
CREATE VAULT MongoDBVault;
Store the required Security Config into the vault:
WRITE INTO MongoDBVault ( vaultKey: "SecurityConfigWithoutKeystore", vaultValue : "TrustStore:Platform/UploadedFiles/truststore.ks;TrustStorePassword:admin1" ); WRITE INTO MongoDBVault ( vaultKey: "SecurityConfig", vaultValue : "KeyStore:Platform/UploadedFiles/keystore.ks;TrustStore:Platform /UploadedFiles/truststore.ks;TrustStorePassword:admin1;KeyStorePassword:admin1" ); WRITE INTO MongoDBVault ( vaultKey: "SecurityConfigPKCSKeyStore", vaultValue : "KeyStore:Platform/UploadedFiles/keystore.ks;TrustStore:Platform /UploadedFiles/truststore.ks;TrustStorePassword:admin1;KeyStorePassword:admin1; KeyStoreType:PKCS12" );
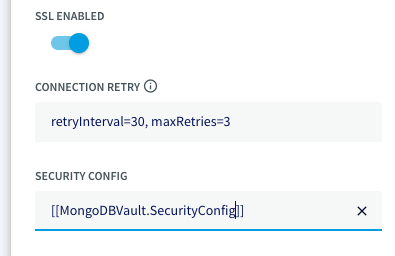
Access the Security Config using the vault name and key directly from the adapter.
Use the vault key and value in the format [[MongoDBVault.SecurityConfig]]:
 |